

Technology & Architecture
JQRBT's technology architecture is the cornerstone of its core competitiveness. We adopt an advanced, robust, and scalable design philosophy aimed at delivering financial-grade performance, reliability, and security.
System Architecture Diagram
JQRBT employs a modern, service-oriented, distributed Microservices Architecture. This approach decomposes the complex system into a series of independent, separately deployable, and scalable service units, enhancing system flexibility, maintainability, and fault tolerance.
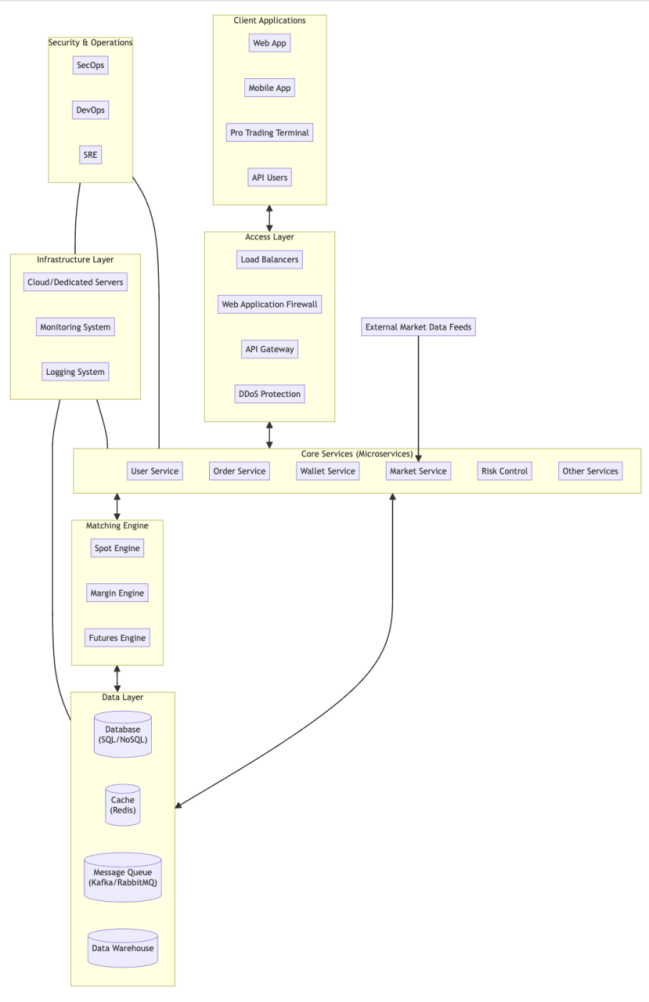
Key Component Breakdown:
This architectural design ensures that the JQRBT trading platform possesses high performance, high reliability, high security, and scalability, capable of handling growing user demands and transaction volumes.

Designed to process millions of orders per second (Millions TPS), effortlessly handling trading pressure during peak market periods.

Core matching logic completes in microseconds, with end-to-end latency from order receipt to trade result generation controlled within milliseconds.

Strictly adheres to the Price-Time Priority matching principle, ensuring all orders are processed fairly.

Core matching logic runs in memory for maximum processing speed, coupled with reliable persistence mechanisms to ensure data safety in unexpected situations.

Employs redundancy designs like primary-standby or multi-active setups to ensure continuous matching service and avoid single points of failure.

Likely developed using high-performance compiled languages such as C++, Rust, or Java, combined with efficient in-memory data structures and concurrent processing models.
We understand the critical need of programmatic traders and partners for powerful, stable, and easy-to-use APIs. JQRBT will provide comprehensive, standardized API interfaces to meet the requirements of various user types.
API Type Comparison:
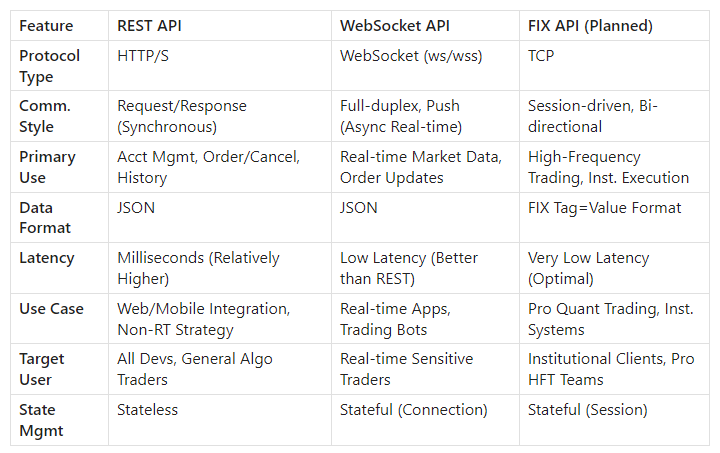
Key API Features:
By offering diverse API options and robust developer support, JQRBT aims to empower developers and institutional clients, fostering a thriving programmatic trading ecosystem.

The microservices architecture allows independent scaling of service instances based on load, enabling elastic scalability. Critical components like the matching engine and market data service also support horizontal scaling.

Critical services and data stores employ redundant deployments (e.g., across availability zones) to eliminate single points of failure. Databases, caches, and message queues are configured with high-availability solutions.

Inter-service communication utilizes mechanisms like circuit breaking, service degradation, and retries to isolate failures and ensure the stability of core functions.

Strict data backup policies (including real-time backups, periodic snapshots) and a comprehensive Disaster Recovery Plan are implemented to ensure the safety of user data and transaction records.


